|
| Chest of Saint Simeon in Zadar, 1377-1380 |
The coronation of King Koloman as King of Croatia in 1102, an act which established the Hungarian-Croatian personal union, was one of the formative events of the Middle Ages for the region. Starting from this point, the two countries were ruled by the Hungarian Kings - although control over the Dalmatian coast was lost for long periods to the Republic of Venice. Currently, and exhibition is on view in Zagreb to illustrate highlights of the common history of the two countries. This joint project of the Hungarian National Museum and the Galerija Klovićevi Dvori (Zagreb) will be shown in Budapest at the end of the year as well. The goal of the exhibition project is to present the Croatian-Hungarian cultural and cultural-historical relations in a broad and illustrative context, thus strengthening the feeling of belonging together in the two nations. The exhibition is divided into eight chronological and thematic chapters, starting with the Middle Ages and continuing with the Renaissance period. Later on, in the early modern times, heraldic representation of the Croatian-Hungarian state community was somewhat special, the relationship of the partner countries manifested in many different ways. In the Baroque era, the veneration of the Hungarian holy kings was lively in both countries. Several examples from the iconographic program and liturgical objects of the Zagreb Cathedral are showcased to highlight this common cult. A special unit is dedicated to the most emblematic family of the era, the Zrínyis/Zrinskis. Their activities in the spirit of dual patriotism left an indelible mark on the culture and art of the two countries. Other sections focus on more modern periods.
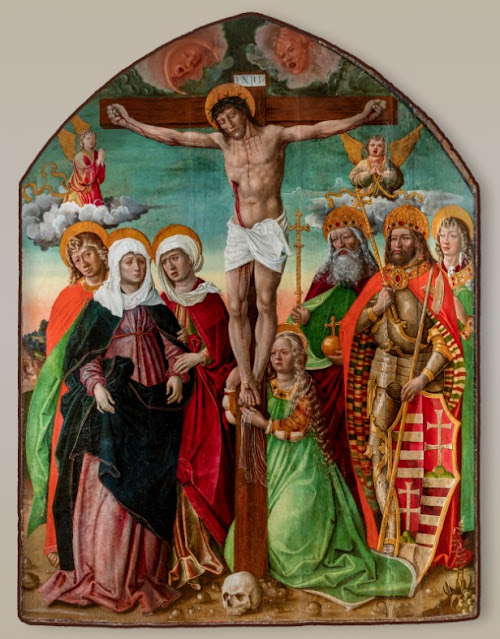 |
| Gianfrancesco da Tolmezzo: Crucifixion with Hungarian saints. Zagreb, 1505 |
A virtual exhibition was also created to present chief objects. The virtual exhibition, currently consisting of 60 objects, guides the visitor - partly chronologically and partly thematically - through the representative spaces of the Hungarian National Museum, the Dome, the Ceremonial Hall, and the Fireplace Halls. CLICK HERE to start the virtual exhibition, then select the English language version.
ARS ET VIRTUS. CROATIA - HUNGARY. 800 YEARS OF COMMON HERITAGE
Virtual exhibition of the Hungarian National Museum, 2020